A Silent Threat: Periodontal Disease and its Shocking Link to Heart Attacks
 By: Britely
By: Britely
As science continues to progress, the intricate connections between different aspects of our well-being continue to unravel. One such revelation that has emerged in recent years is the alarming link between periodontal disease and an increased risk of heart attacks. According to the National Library of Medicine, individuals over the age of 55 with periodontal disease face a staggering 200% higher risk of experiencing a heart attack. This revelation serves as a stark reminder that oral health is not isolated but is deeply intertwined with our overall physical well-being.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums and bone. It often begins with gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe stage where pockets form between the teeth and gums, leading to further inflammation and potential tooth loss.
The Heart-Oral Health Connection
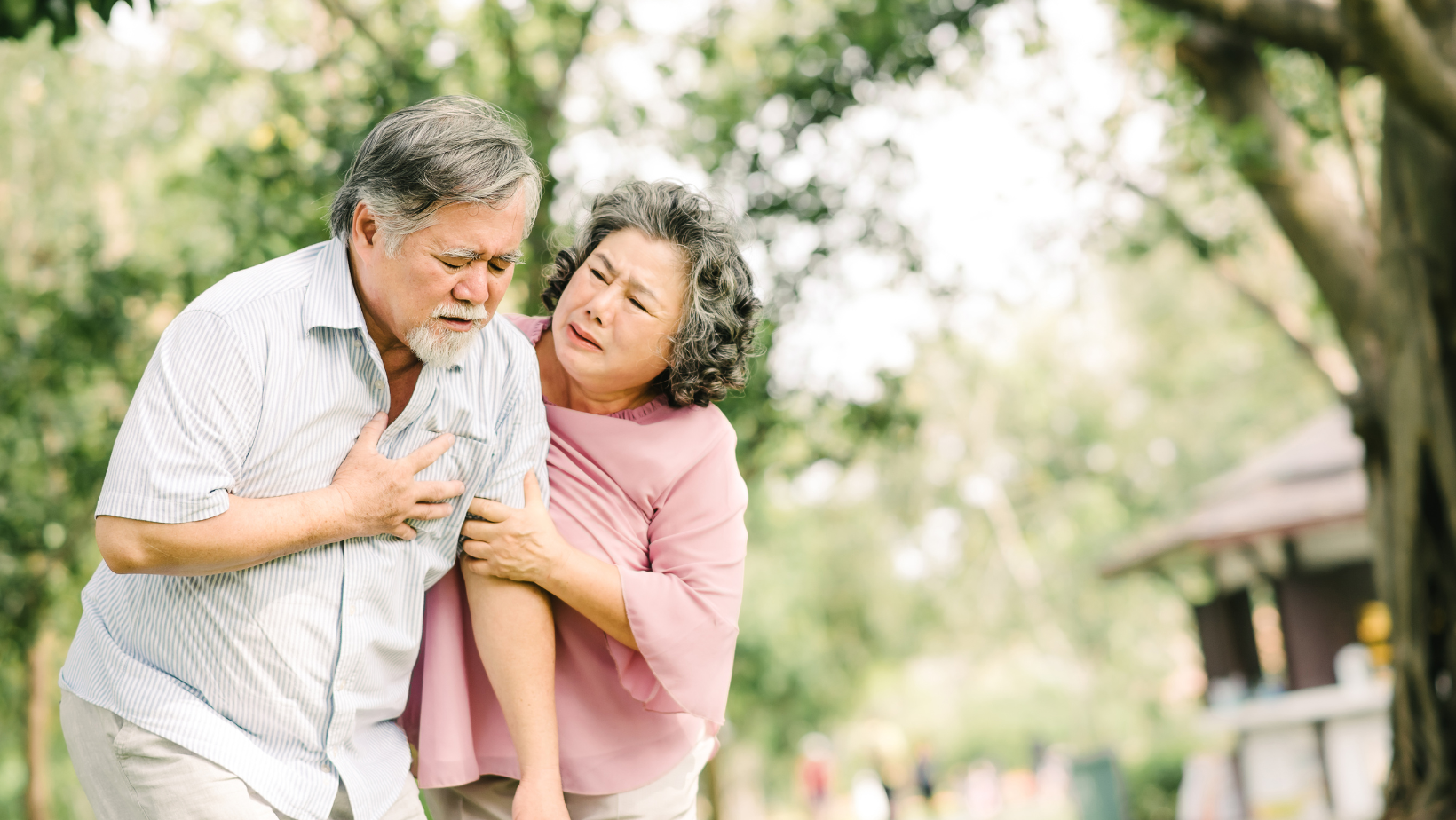
The connection between periodontal disease and heart attacks lies in the inflammatory response triggered by the bacteria present in the infected gums. Chronic inflammation is a known contributor to atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can ultimately lead to heart attacks and other cardiovascular events.
As the body fights the oral infection, the inflammatory compounds released can enter the bloodstream, contributing to systemic inflammation that is detrimental to cardiovascular health. Additionally, the bacteria associated with periodontal disease may directly contribute to the formation of arterial plaques, further compromising heart health.
The Age Factor
The heightened risk for heart attacks in individuals over the age of 55 underscores the importance of addressing periodontal disease, particularly as we age. As people grow older, they may be more susceptible to gum disease due to factors such as decreased immune function, reduced saliva production, and a higher likelihood of chronic medical conditions.
Prevention and Management
Preventing periodontal disease not only safeguards oral health but may also contribute to reducing the risk of heart attacks. Regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and diligent oral hygiene practices, including brushing and flossing, are essential components of maintaining healthy gums.
For those already grappling with periodontal disease, early intervention is crucial. Scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and other dental treatments can help manage the condition and prevent it from progressing to more severe stages. Integrating lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet and quitting smoking, can further support overall cardiovascular well-being.
The revelation that periodontal disease can significantly increase the risk of heart attacks, especially in individuals over the age of 55, serves as a wake-up call to prioritize oral health as an integral part of our overall well-being. As the medical community continues to explore the intricate links between different aspects of health, it becomes increasingly clear that maintaining healthy gums can be a vital step in safeguarding our hearts. Regular dental care, early intervention, and lifestyle adjustments are key components in breaking the connection between periodontal disease and heart attacks, empowering individuals to take control of their health and well-being.