Unraveling the Relationship Between Periodontal Disease and Diabetes
 By: Britely
By: Britely
Periodontal disease and diabetes are two prevalent health issues that, at first glance, may seem unrelated. However, more and more research suggests a complex interplay between these conditions, each influencing the other in ways that can significantly impact an individual’s overall health. How can the presence of one condition exacerbate the other, and vice versa?
The Bidirectional Link: Diabetes and Periodontal Disease
Research indicates a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease, with each condition negatively influencing the progression and severity of the other. Uncontrolled diabetes, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, has been identified as a significant risk factor for the development and progression of periodontal disease.
Impact of Diabetes on Periodontal Disease
Diabetes affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to increased levels of glucose in the saliva. This elevated glucose provides an ideal environment for bacteria in the mouth to thrive, leading to the formation of plaque and tartar. Moreover, diabetes compromises the immune system, reducing the body’s ability to combat infections, including those in the gums.
As stated by Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, uncontrolled diabetes can make it harder to control periodontal disease, contributing to inflammation, bleeding gums, and tooth loss. The link between diabetes and periodontal disease goes beyond oral health, with systemic inflammation and increased levels of cytokines potentially worsening diabetes-related complications.
Impact of Periodontal Disease on Diabetes
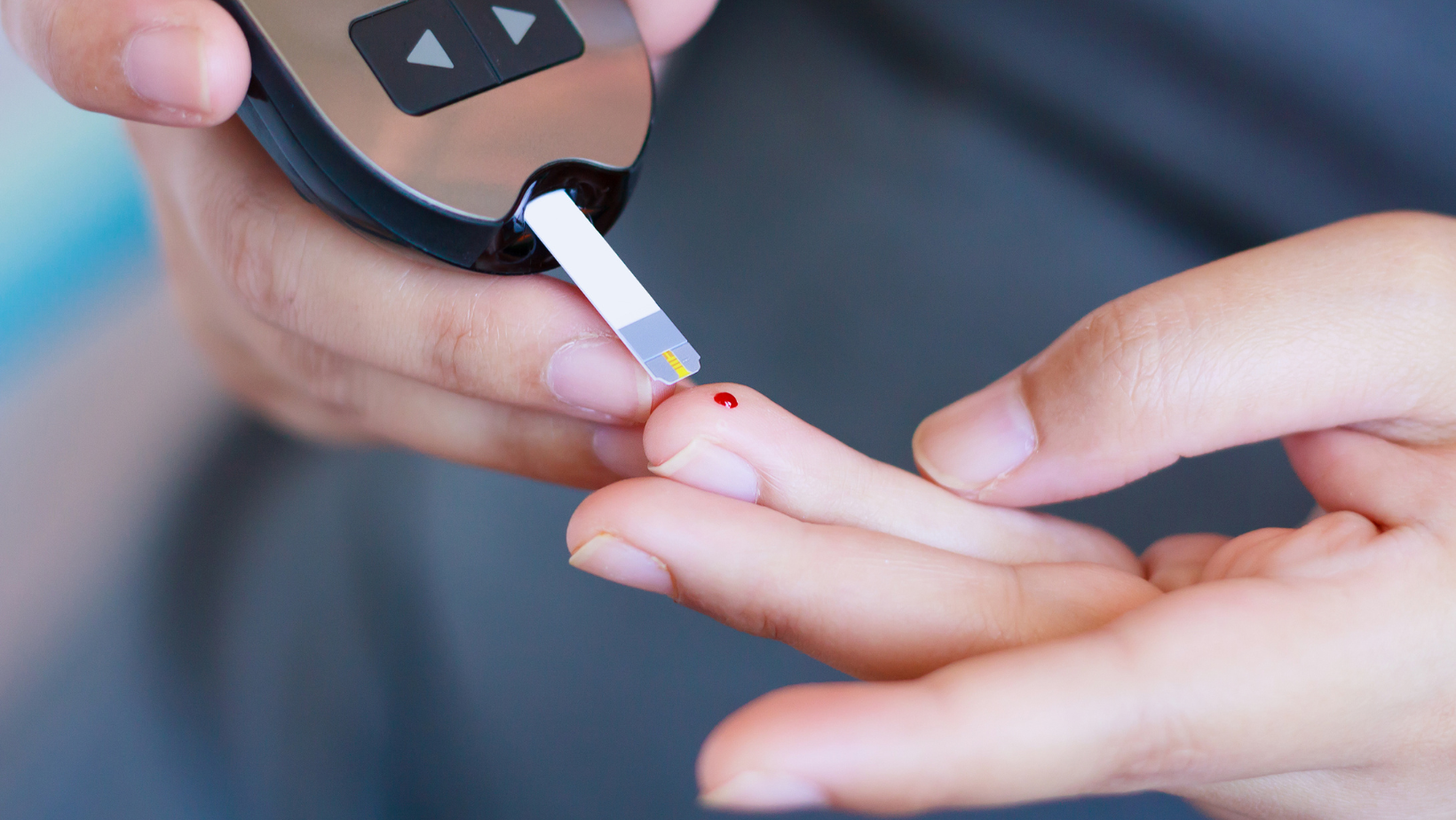
On the flip side, periodontal disease can adversely affect diabetes management. Chronic inflammation resulting from gum disease can lead to insulin resistance, making it more challenging for individuals with diabetes to control their blood sugar levels. Research suggests that treating periodontal disease may lead to improved glycemic control in diabetic patients.
The connection between periodontal disease and diabetes is not solely based on the oral cavity. The systemic inflammatory response triggered by gum disease can contribute to insulin resistance and hinder the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies.
The link between periodontal disease and diabetes is a dynamic and complex relationship that underscores the importance of holistic healthcare. Understanding how these conditions influence each other is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. It highlights the need for an integrated approach to managing both diabetes and periodontal disease to improve overall health outcomes.
As research continues to unveil the intricate connections between oral health and systemic conditions, individuals with diabetes and those at risk for periodontal disease should prioritize regular dental check-ups, maintain good oral hygiene practices, and work closely with healthcare professionals to manage both conditions effectively. By addressing the bidirectional impact of diabetes and periodontal disease, we can take significant steps toward improving overall health and well-being!