The Surprising Link Between Tooth Loss and Dementia
 By: Britely
By: Britely
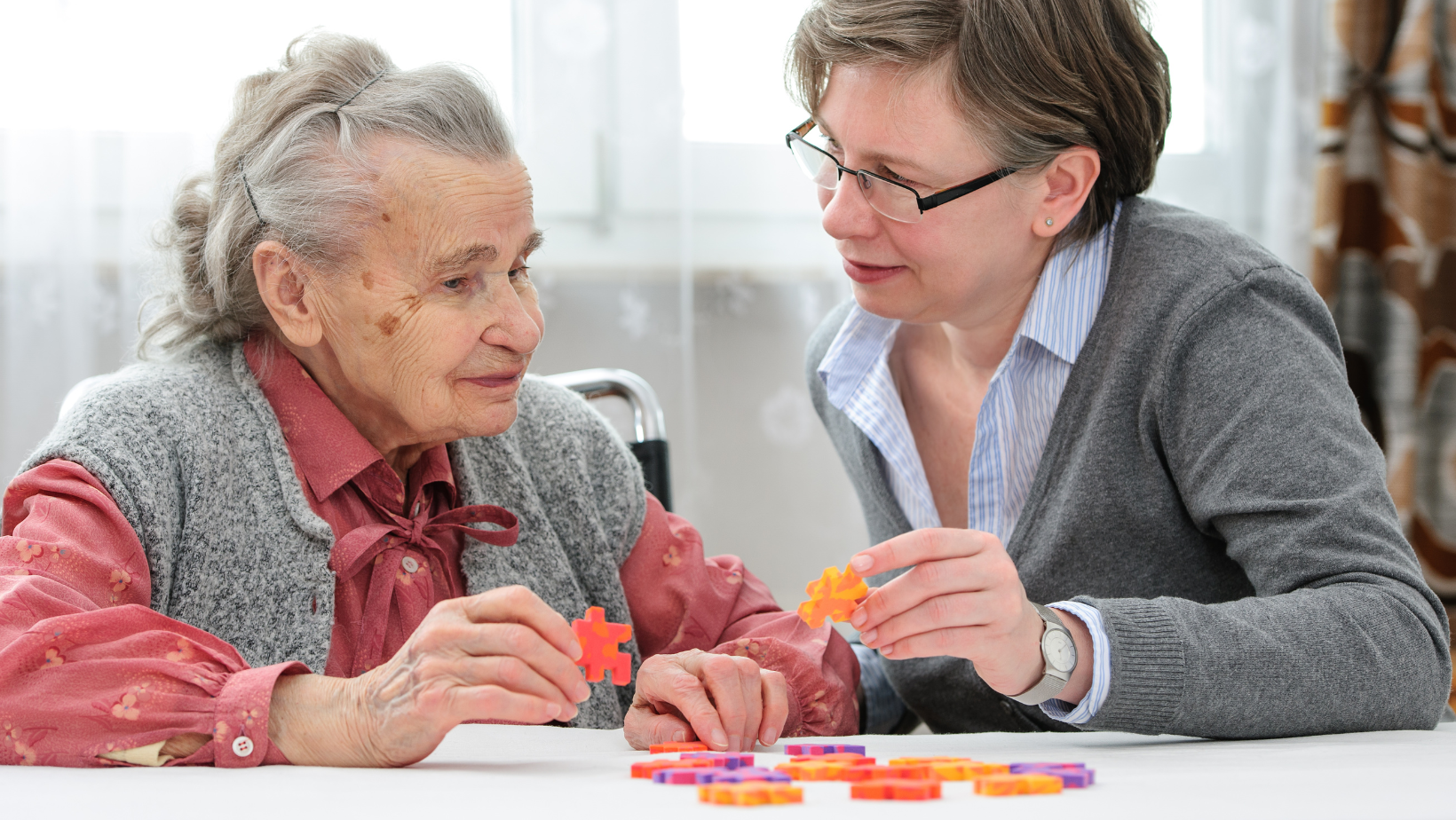
As we age, it’s no surprise that our bodies go through natural changes. One area that often receives less attention than others is dental health. However, recent research has shed light on a surprising connection between tooth loss and cognitive decline. According to a study conducted by Harvard Health, adults who have lost eight or more teeth face a 48% higher risk of cognitive impairment and a 28% higher risk of dementia. These findings emphasize the importance of not only maintaining good oral health but also the potential impact it has on overall cognitive function.
Understanding the Study
The study conducted at Harvard Health involved analyzing data from over 8,000 participants aged 50 and above. Researchers tracked the participants’ dental health and cognitive function over an extended period. The study found a clear correlation between tooth loss and cognitive decline, leading to a greater risk of cognitive impairment and dementia.
Reasons for the Link
Several factors are believed to contribute to the association between tooth loss and cognitive decline. One explanation is related to the role of inflammation in both dental and cognitive health. Periodontal disease, a common cause of tooth loss, activates inflammatory responses that can spread throughout the body, including the brain. Chronic inflammation is believed to play a significant role in the development of various cognitive disorders.
Another possibility is that tooth loss negatively impacts an individual’s overall quality of life. People with significant tooth loss may experience difficulties in eating and speaking, leading to dietary restrictions and social isolation. These factors can contribute to feelings of depression and anxiety, which are known to affect cognitive function.
The Importance of Oral Health
Maintaining good oral health is crucial for several reasons, and this study highlights yet another benefit. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and a well-balanced diet can minimize the risk of tooth loss. By keeping our teeth and gums healthy, we may also reduce the chances of developing cognitive impairments later in life.
Additionally, addressing dental issues promptly can positively impact overall well-being. Seeking professional help as soon as dental problems arise can help prevent complications and ensure early intervention in potential cognitive decline.
The connection between tooth loss and cognitive decline is a significant finding that highlights the importance of oral health throughout life. Taking steps to maintain good dental hygiene can potentially play a role in reducing the risk of cognitive impairments and dementia as we age. By prioritizing oral health, we not only improve our smiles but also contribute to our overall physical and cognitive well-being.
Remember, regular visits to the dentist, proper oral hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in safeguarding both our pearly whites and our cognitive function for years to come.